SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES OF LAST YEAR
Added on: 21st Oct 2016
RESEARCHERS DESIGNED NANO MEDICINE
FOR TREATING BREAST CANCER
Iranian nanotechnologists synthesized the latest scheme Nano
pill of bio-adaptable and biodegradable chain molecular
that is able to ebb toxicity of anti-cancer drugs. This modern
medicine is being considered for treating breast cancer
in a more effective way than any previous treatment
but only time will verify this.
SCIENTISTS REPROGRAMMED PLANTS FOR
DROUGHT TOLERANCE

Scientists have genetically reprogrammed plants to be drought
tolerant in response to an already existing agrochemical,
circumventing the need for a new chemical that would
otherwise have required many years of testing.
THE WORLD’S FIRST “THREE-PARENT” IVF
BABIES BECAME A REALITY

Last February the British government voted to allow a
controversial new technique involving babies created
by three people. The UK intends to become the first place
in the world to offer this medical procedure, which can
also be used to treat mitochondrial diseases.
NASA’S KEPLER MARKED THE ONE THOUSANDTH
EXOPLANET DISCOVERY

Last January NASA announced the one thousandth confirmed
exoplanet discovered by the Kepler Space Telescope. Three
of the newly confirmed exoplanets were found to orbit
within habitable zones of their related stars: two of the three,
Kepler-438b and Kepler-442b, are near-Earth size and
likely rocky; the third, Kepler-440b, is a super Earth.
SCIENTISTS MAPPED BOWHEAD WHALES GENOME

Scientists from the United States and the UK mapped the
genome of the bowhead whale and identified genes
responsible for its two hundred year life span, the
longest of any mammal. The genome mapping was a result
of two separate studies carried out in the States and
the UK that allowed scientists to identify a small number
of genes linked to cancer resistance, DNA damage
repair, and increased longevity.
NEW ROLE FOR PROTEINS
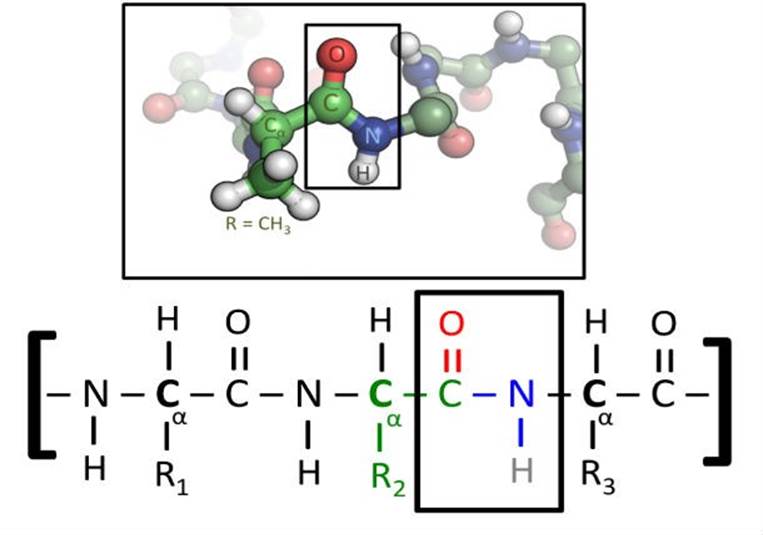
A study published in Science showed evidence that a
protein partially assembles another protein without
genetic instructions. Defying textbook science, amino acids
(the building blocks of a protein) can be assembled by
another protein and without genetic instructions.
HIV VACCINE
The fight against HIV and AIDS took a huge step forward in
2015 when researchers at the Scripps Research Institute
developed a vaccine that was incredibly effective against
HIV-1, HIV-2, and simian immunodeficiency virus. The
key difference here is the new HIV vaccine actually alters
DNA to fight off the virus rather than injecting a weakened
form into the body so the immune system can learn to
fight it. The research is still in the early stages, but the
results thus far are extremely promising and if they
continue to be, HIV treatment will become far simpler.
BRAIN IMAGING MAY HELP PREDICT FUTURE BEHAVIOUR

A review article published in the journal Neuron described a
number of recent studies showing that brain imaging can
help predict a person’s future learning, criminality, health
related behaviours and response to drug or behavioural
treatments. The technology may offer opportunities
to personalize educational and clinical practices.
FIRST CONTRACTING HUMAN MUSCLE GROWN
IN A LABORATORY
In a laboratory first, Duke researchers have grown a
human skeletal muscle that contract and responds
just like native tissue towards external stimuli, such as
electrical pulses, bio chemical signals and pharmaceuticals.
The lab grown tissue should soon allow researchers
to test new drugs and study disease in functioning
human muscles outside the human body.

Comment on this